News
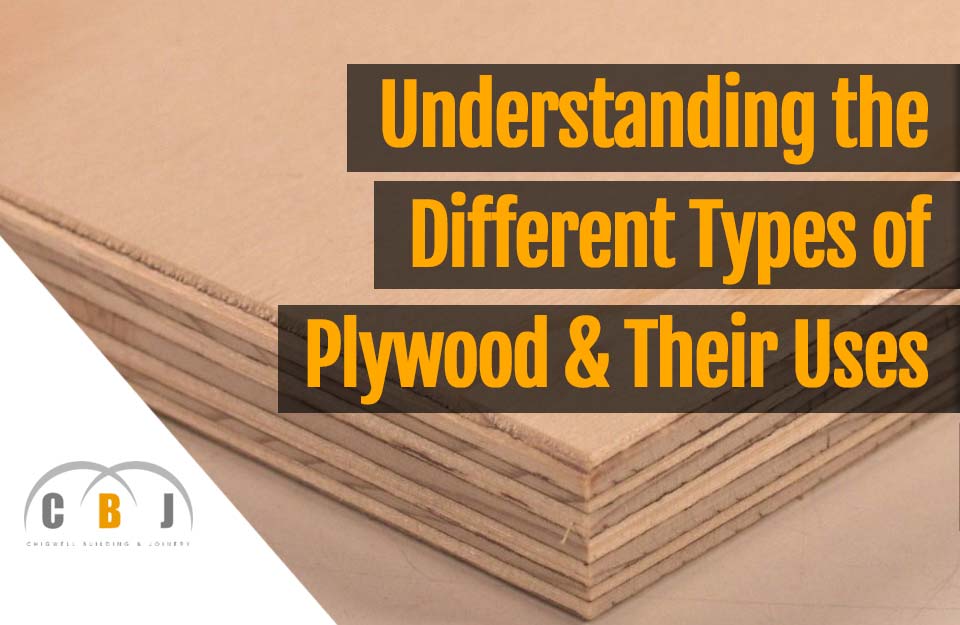
Understanding the different types of plywood and their uses
Author Chigwell Building & Joinery
Date 10/05/2017
When and how to use this versatile timber product
Enter into any recently constructed building project and chances are, you’re never too far away from some form of plywood, whether visible or most likely hidden from view. As an incredibly popular material, plywood tends to be used in construction not only because it is cost effective, but it is also extremely versatile, strong and reliable.
In essence, plywood is a simple engineered product consisting on several thin sheets of timber, glued in layers at 90º angles to the corresponding layer above and below and compressed together at high pressure. This forms a strong, hardwearing material than can stand the test of time and be used is many projects that demand strength and durability.
Because it is so versatile, plywood can be found used in various items including furniture, flooring, partitions, external walls and roofs. Even in some high end cabinetry.
Key properties of plywood
Plywood has a number of core properties that make it unique to any other building material including:
Strength
Due to its layered construction, plywood tends to be far stronger than traditional timber. The simple engineering process of glueing thin layers of alternating grains prevents the board from snapping or breaking under pressure. The general rule of thumb ism, the thicker the ply, the stringer it is.
Stress Resistance
Engineered plywood is capable of withstanding much heavier weight and pressure that an equivalent sheet of standard timber and thus, can handle greater stress. A heavy object placed onto a single sheet of timber would lead to bending and eventual breakage whilst plywood would spread the load over a larger surface due to it’s layered construction, with the grain direction alternating at each layer.
Flexibility
Plywood is also very flexible and bendy if needed as it can be constructed at pretty much any given thickness, from a few millimetres to several centimetres thick. That is why thin plywoods tend to be used on demanding projects that require a curved surface such as ambitious internal wall projects or skateboard ramps that were made famous during the 1980’s.
Moisture Resistance
In certain plywoods, the glue used to construct the layers is water repellant so even if used externally where moisture and humidity levels fluctuate, it will not warp, expand, shrink or delaminate. This makes it the ideal material for outdoors projects where it needs to last for several years.
Insulation
Not many people realise that plywood has the added benefit of being a very good insulator and soundproofing material. The layers naturally make it a good thermal product so if used correctly, is a great way to reduce heating bills and noise pollution from room to room.
How many types of plywood are there?
There’s a variety of different types of plywood for different applications including:
Softwood Ply
The most common manufactured plywood, that comes in a variety of thickness is often used on construction projects.
Hardwood Ply
More commonly used for more hardwearing projects that demand longevity, and constructed from stronger timbers, hardwood ply is ideal for more demanding jobs.
Flexible Ply
Usually constructed from just a few plies, these boards offer greater flexibility for projects that require curved surfaces.
Marine Ply
As the name suggests, this ply is used on marine-based applications due to its water resistant properties.
Aircraft Ply
To add greater heat resistance properties, this ply is constructed from birch.
Decorative Ply
Used where the wood grain will be on show, this ply tends to be made from beautiful woods including oak and rosewood to construct furniture and bespoke finishes.